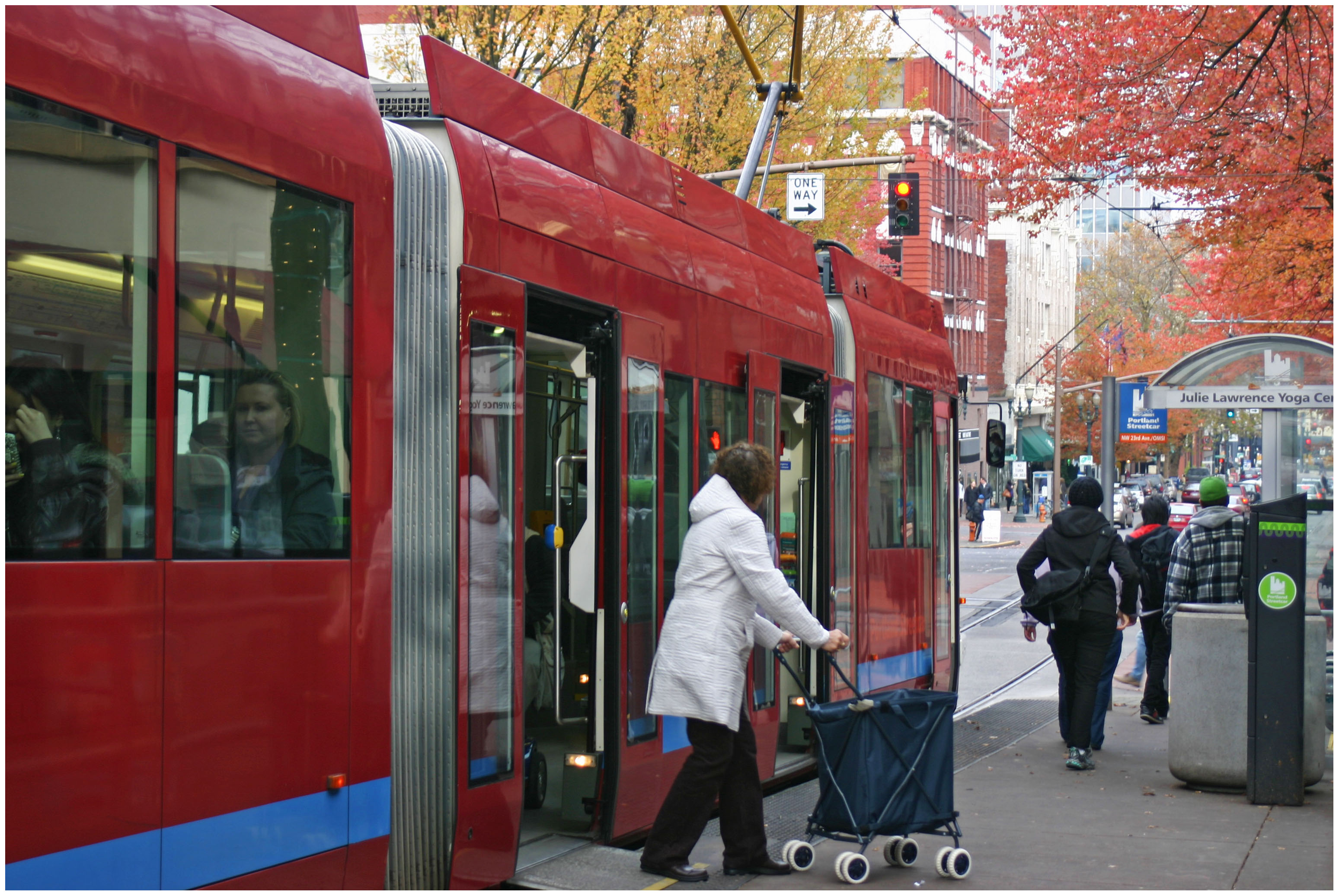
Six months ago Portland celebrated the opening of a 3.3-mile extension of their modern streetcar system across the Willamette River.
The $148.3 million Portland Streetcar project represents a significant expansion of the existing six-mile system, and city leaders hope it will find similar success in the Lloyd District, Buckman and Hosford-Abernethy neighborhoods as it has in the Pearl District and Northwest District.
At the time when Portland built its first streetcar leg, the Pearl District was a rundown industrial district in search of new life, and the Northwest District was looking to build on its existing stability.


Portland’s Pearl District [LEFT] has seen a massive transformation over the past decade, and many hope the streetcar’s recent extension will do the same for the city’s Buckman neighborhood [RIGHT]. Photographs by Randy Simes for UrbanCincy.
The story is not all that different on the east side of the river where the Buckman and Hosford-Abernethy neighborhoods are looking for the streetcar to breathe new life into its underutilized land and lingering industrial users, and the Lloyd District is trying to build on its successes and possibly reinvent itself with a lesser focus on the automobile.
While the streetcar extension is operating daily, the investments are not quite finished. Transportation officials are waiting on an additional six streetcar vehicles to roll off the production line so that service frequencies can be improved for the system’s four million annual riders.
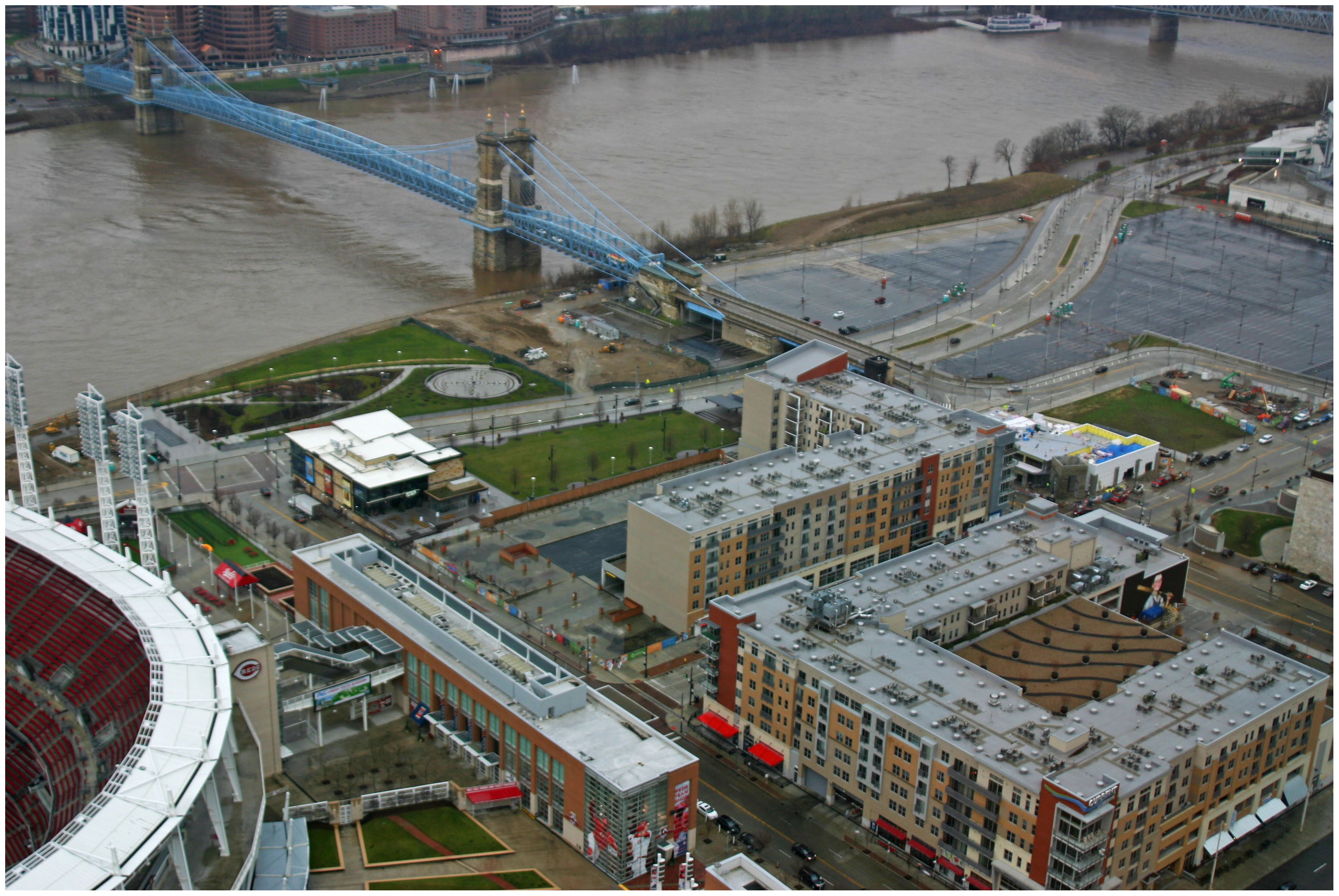
TriMet officials are also overseeing progress on the construction of the new Portland-Milwaukie Bridge which will provide a river crossing for bicycles, pedestrians, streetcars, and light rail from Hosf0rd-Abernethy to the South Waterfront District as part of a the 7.3-mile Portland-Milwaukie Light Rail Project.
The $134 million bridge project is expected to open in September 2015 and buoy both new and existing ridership on the city’s light rail and streetcar systems.


Construction progresses on the Portland-Milwaukie Light Rail Bridge in November 2012 [LEFT], which will connect the Hosford-Abernethy neighborhood with the South Waterfront District [RIGHT]. Photographs by Randy Simes for UrbanCincy.
The verdict is still out on whether or not the new east side streetcar extension will have as big of an impact as it did on the west side of the river next to downtown, but the possibilities are there.
The streetcar’s alignment through Buckman and Hosford-Abernethy heads south along Martin Luther King Boulevard and north a block over on Grand Avenue. To the west of MLK Boulevard is the river with a large collection of warehouses in between. To the east of Grand Avenue is an in-tact neighborhood that has become increasingly popular with young creative types over the past several years.
In between the two streets one will find a collection of aging car dealerships and associated service businesses that date back to the mid-twentieth century.
These large parcels, combined with the large warehouse properties immediately to the west, offer a unique opportunity for large scale redevelopment. Such massive real estate investment might not be plausible without another real estate bubble.
The prospects are there, however, and if Portland can pull off even a fraction of the investment in Buckman as they saw in the Pearl District, then the city will add billions of dollars to its real estate value and create a secondary downtown in the city center for the 2.2 million person region.