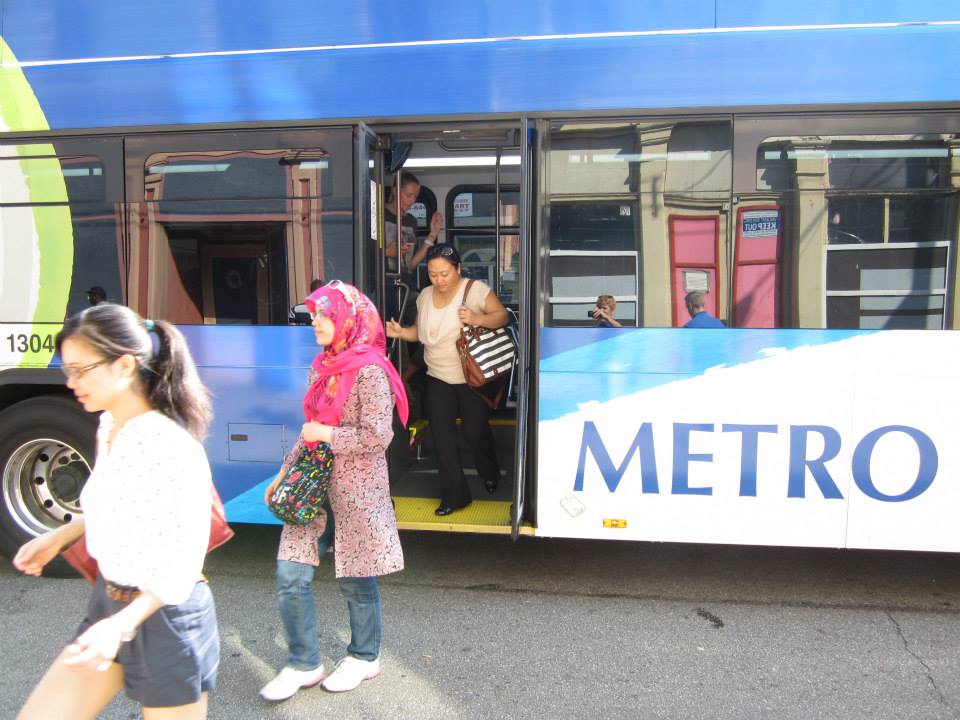
Over the past month, Metro has been hosting public listening sessions in order to get a better idea for what current and would-be transit riders are looking for out of the region’s largest transit provider.
While the five sessions have been completed, Metro is still accepting feedback through an online survey that takes about five minutes to complete. Agency officials have not said when that process will be closed, but they say that the goal is to compile the data by the end of the year.
This public feedback process falls in line with growing speculation that Metro will ask Hamilton County voters next fall to approve a sales tax increase that would pay for expanded bus service throughout the county. As it is now, Metro is almost exclusively funded by the City of Cincinnati, and thus primarily provides service within those boundaries. Service outside of those boundaries costs riders extra – a situation that would be removed should voters approve the sales tax increase.
“At the end of the day, the transit system belongs to the people,” explained Jason Dunn, SORTA Board Chair. “It is our job to be good stewards of the transit system and uphold its mission. Ultimately, we’ll use this feedback to help us make decisions that will set the agenda for transit in the future.”
The public is asked to weigh in on a number of key items in the survey, including where bus service should be extended, and what kinds of operating schedules are preferred. The survey also asks about whether real-time arrival display boards, enhanced shelters and ticketing machines would be desired. All of these are items Metro has been adding over recent years, but at a modest pace.
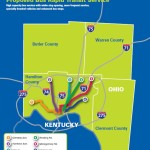
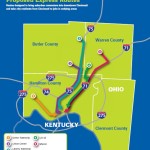
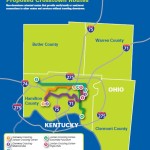
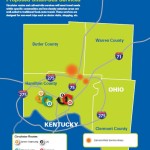
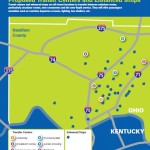
In relation to service operations, Metro officials ask about adding more direct crosstown routes, park-and-ride lots, operating buses earlier or later, increasing weekend frequencies, and adding service to major commercial corridors like Glenway Avenue, Hamilton Avenue, Vine Street, Reading Road and Madison Avenue.
Each of these corridors have been identified for more robust service akin to what has been done along Montgomery Road, which features the first Metro*Plus route in the region. While not full-blown bus rapid transit, Metro officials see it as a step in that direction with its more frequent service, enhanced bus shelters and less frequent stops that allow for faster travel.
Of course, without a dedicated regional transit tax many of these improvements will be difficult to accomplish, or take many years to realize. In the most recent round of TIGER funding, Cincinnati did not apply for any transit-related projects, nor did it even compete for any funds in the recent distribution of the FTA’s Transit-Oriented Development Planning Pilot Program.
While City Hall focused its TIGER grant applications on the Elmore Street Bridge and Wasson Way, both of which were unsuccessful, Metro officials said they did not apply for the FTA funds because they did not believe they had projects ready for successful consideration. But some local transit advocates disagree.
“Our elected officials and administrators are asleep at the wheel,” said Derek Bauman, Southwest Ohio Director of All Aboard Ohio and Chair of Cincinnatians for Progress. “Pools of money exist, particularly at the federal level, for all types of transit planning and construction. We must at accept that times have changed, prepare for the modes of transportation that people are demanding today, and then avail ourselves to resources to make it happen as they become available.”
An additional meeting will be held to gather public feedback from young professionals on Wednesday, November 11 from 6pm to 7:30pm at MORTAR Cincinnati in Over-the-Rhine. Metro CEO and General Manager Dwight Ferrell will be there to take part in the Q/A, and the first 50 people in attendance will receive a free $10 stored value bus pass.
Metro officials say that all of the feedback from the listening sessions and online survey will be considered by the newly created Metro Futures Task Force, which is made up of community leaders who will then present their findings to the SORTA Board in early 2016.
EDITORIAL NOTE: This story has been updated to reflect an additional public meeting that will be held on the evening of Wednesday, November 11.