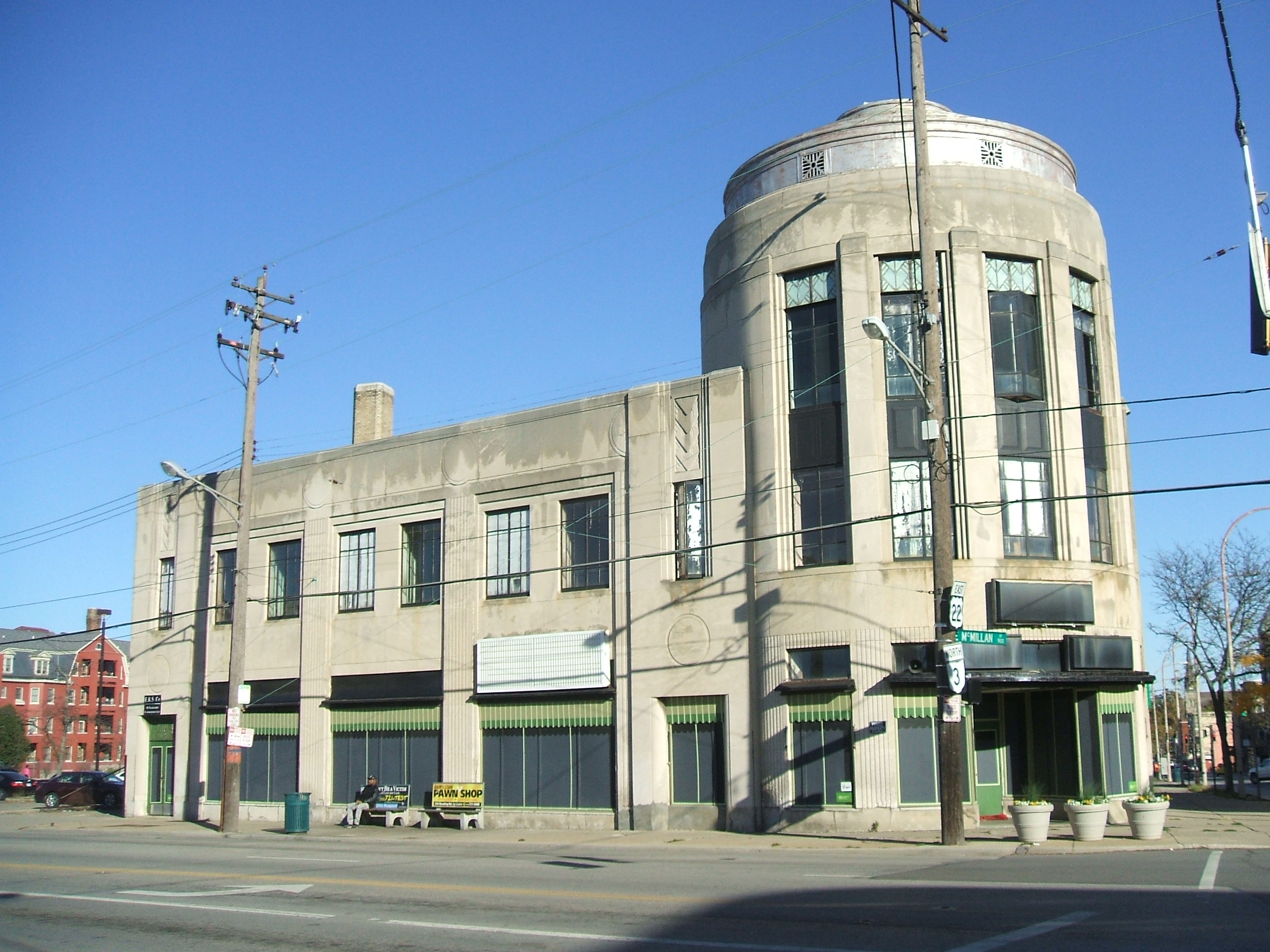
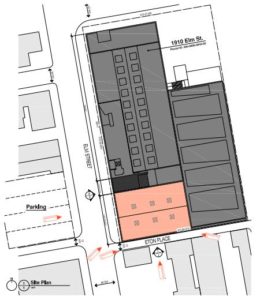
Another development is coming to the Brewery District. The Historic Conservation Board approved a zoning variance that will bring fifty affordable housing units and a restaurant to several vacant buildings along the streetcar line.
Affordable housing in Over-the-Rhine (OTR) has received a lot of press recently. Freeport Row, the newly-christened Source 3 development at Liberty and Elm, was heavily criticized because it lacked any affordable housing. Most recent development has been market-rate or luxury apartments, despite the fact that OTR’s average median income was $14,517 in the 2010 census.
The fears aren’t unfounded; the neighborhood has lost affordable housing. Xavier Community Business Institute determined that OTR and Pendleton have lost 2,300 affordable housing units since 2002. This project — called Abington Flats — will help replenish that stock. Three different companies banded together to create Abington: 3CDC, Model Group, and Cornerstone Corporation Renter Equity. 3CDC is developing the commercial space, while the other two control the residential space. This project is part of a larger effort by the team to develop hundreds of affordable units in OTR.
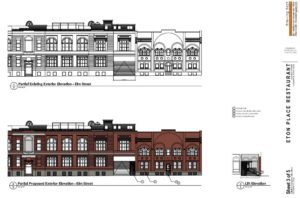
Abington Flats consists of five buildings, the largest of which is 33 Green Street. Built in 1910, the four-story building features a commercial space on the ground floor with three floors of residential apartments above. Model Group Senior Project Manager Jennifer Walke said that all five buildings need “substantial rehab.” 33 Green Street will be 100 percent ADA accessible. The team is shooting for LEED Silver certification.
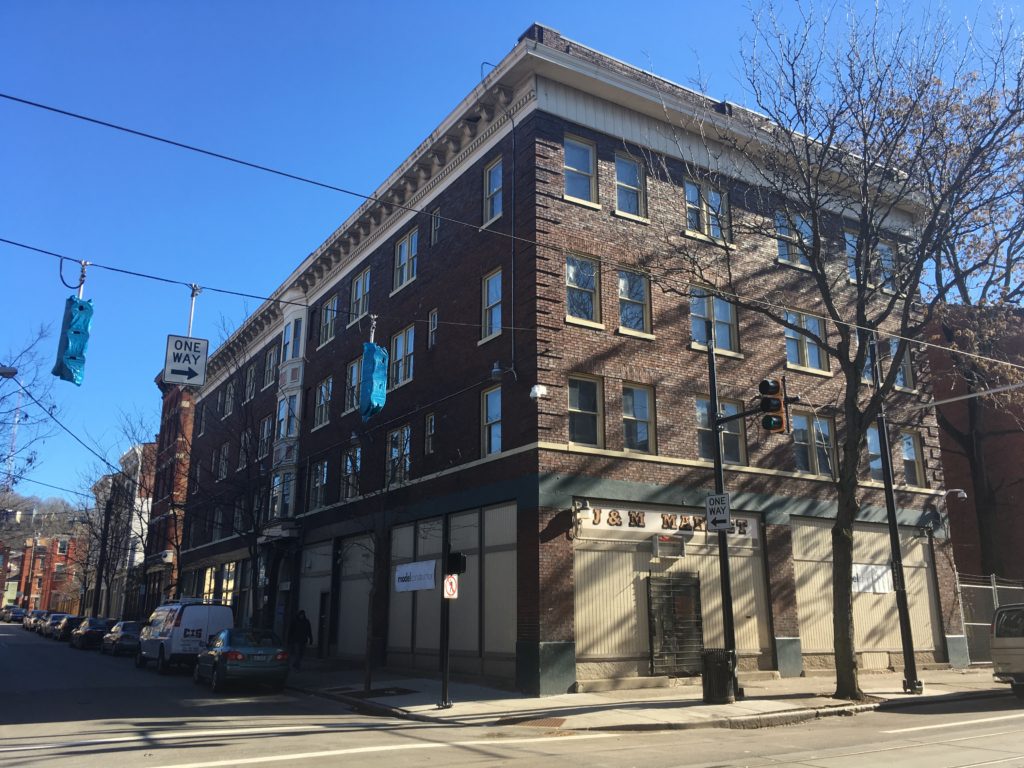

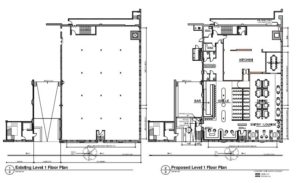
In an email to UrbanCincy, 3CDC Communications Manager Joe Rudemiller said that, depending on future tenants’ needs, there will be up to four retail or office space and up to two restaurants or bars.
Finding a restaurant or bar will be key to the project’s long-term financial viability. Tax credits fund a building’s development and construction; they don’t cover operating costs. Rent from below market-rate units might not cover its full cost. Rent paid by commercial tenants offsets this difference.
This is why investors rarely back affordable housing projects. It’s hard to profit. Plus, tenants with less financial security pose a greater risk to the owners. Cornerstone’s shared equity program strives to overcome this trend. Tenants can earn equity through timely rent payments and property maintenance. Build up enough equity and — after five years — it becomes cash. Abington Flats will use their system.
Total costs hover around $17 million — $13.8 million for the residential portion and $3 million for the commercial space. Several subsidies fueled the development, including Federal and State Historic Tax Credits and Low-Income Housing Tax Credits.