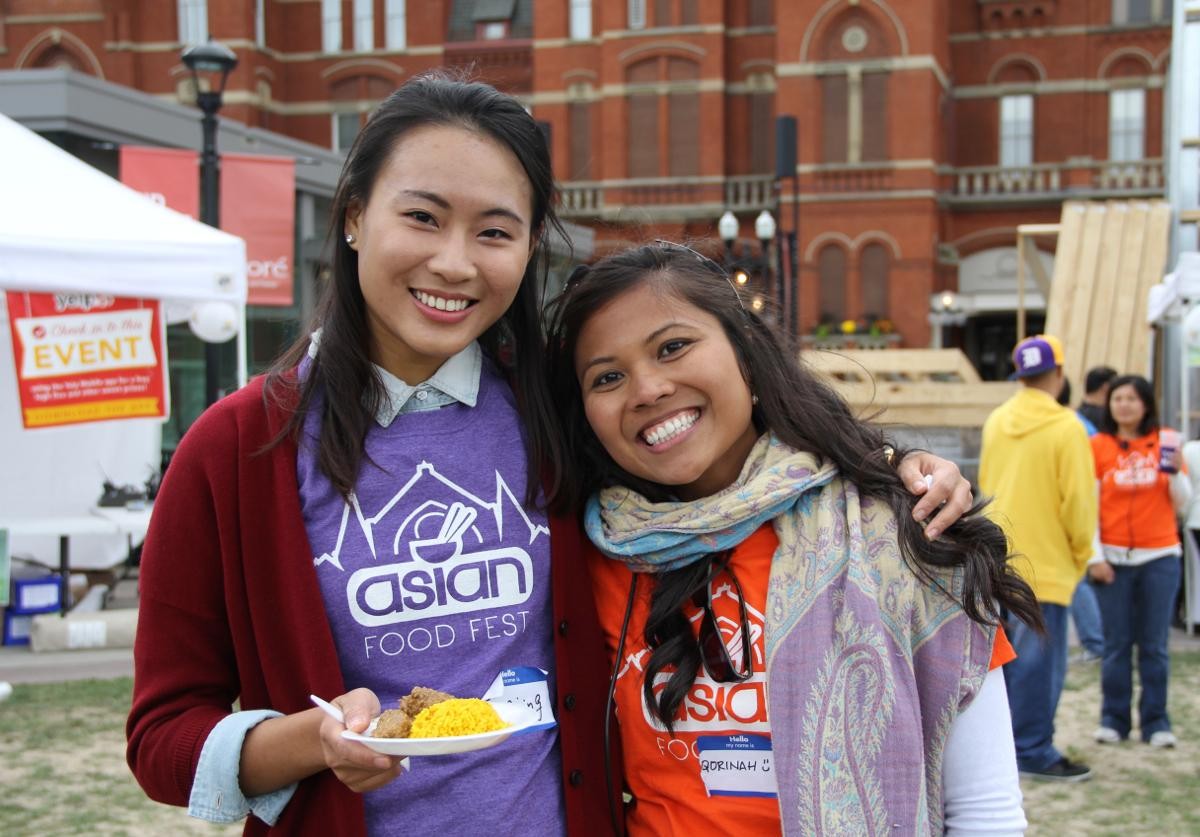
Pho, Pad Thai, Nasi Lemak, Bibimbap. Great Asian cuisine can sometimes be hard to located with it being spread throughout Uptown, Northern Kentucky and northern suburbs like Fairfield or Springdale. However, this weekend many of the best Asian dishes will be available at the sixth annual Asian Food Festival in Washington Park.
This two-day extravaganza will celebrate and feature the diverse and tasty cuisines of Asian countries including Vietnam, Thailand, China, Korea, Malaysia and many more.
Created in 2010 by a diverse group of friends who wanted to spread their love of Asian food and culture, the festival has since been building awareness of the city’s diverse Asian population and food scene.
Over the past six years, the festival has showcased some of the city’s best Asian restaurants and chefs, while fostering connections between community members and local Asian-American organizations and businesses. Past vendors, such as Pho Lang Tang and Huit, have since started retail establishments in the center city; and festival organizers hope the event can play a bigger role in continuing to grow the local Asian food scene.
A new feature at this year’s festival is the “Secret Menu” booth, which will feature unique food from home chefs and aspiring food entrepreneurs.
“This is a special chance for foodies to get a taste of a homecooked Asian meal from local amateur chefs who are excited to share the food they grew up with,” Marketing Director Tessa Xuan told UrbanCincy. “We hope the Secret Menu chefs will gain enough experience to become independent vendors and even restaurant owners someday.”
New vendors this year include Hawaiian food stand Ono Grindz, Clifton-based carryout spot Thai Express, and the West Chester-based Filipino restaurant Dai Trang. And, of course, many crowd favorites will be returning, including the Indonesian Fusion restaurant Huit BBQ, Taiwanese bubble tea cafe Boba Cha, and Red Sesame – the food truck famous for their Korean BBQ Tacos.
Admission to the festival is free, but donations are encouraged – proceeds from the festival will go towards supporting the 501(c)(3) nonprofit Asian American Cultural Association of Cincinnati (AACAC), and to host future Asian cultural events throughout the region.
Asian Food Fest will be held at Washington Park in Over-the-Rhine this Saturday and Sunday. Hours on Saturday are from 4pm to midnight, and Sunday from 12pm to 8pm. The event is free and open to the public, but dishes from vendors will range from $2-$6.
The festival is easily accessible from #21, #64, #78 & #46 Metro bus routes and Cincy Red Bike with a station in the park.