The Ohio Department of Transportation is looking for additional feedback related to transportation improvements for Cincinnati’s eastern neighborhoods and far reaching suburbs.
The survey comes after ODOT has said that they are backing away from original plans for the hotly debated Eastern Corridor project, which came under public scrutiny for its scope and potentially negative impact to established neighborhoods on the city’s east side.
While the project will most certainly not be moving forward as originally envisioned, public officials are still looking to get a grasp on what kinds of investments could be made to improve traffic congestion and mobility options.
So far, ODOT has held public meetings in Newtown and Mariemont, and will hold meetings in Anderson Township, Mt. Lookout, Fairfax and Mt. Washington in the coming weeks – the next of which will occur this evening, from 6pm to 8pm, in Mt. Lookout at Christ The King Parish Center at 927 Ellison Avenue.
Those unable to attend that or the other upcoming meetings, are being encouraged to complete an interactive web-based survey. Taking approximately five to 10 minutes to complete, the survey asks respondents to rank the importance of the types of transportation improvements needed for the corridor, while also asking for specific location-based improvement suggestions.
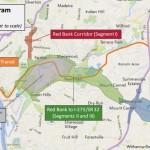
The survey and public feedback for this effort is focused on what ODOT calls Segments II and III of the project, and is not limited to those who live or work in the study area, but rather open to anyone who finds themselves passing through the area.
Early results from the survey show that respondents want ODOT to focus investments on improving public transit, biking and walking options, and travel time through the corridor. While the travel time option could mean many different things, it may be connected to the other two top rankings for multi-modal transportation enhancements.
Projects not specifically mentioned in the survey include the Oasis Corridor commuter rail line, which also has been on the ropes lately, and the Wasson Corridor, which is still unclear how it will proceed with respects to a trail only, or a light rail and trail combination.
As UrbanCincy wrote in June 2015, a new local access bridge crossing the Ohio River, from Columbia Tusculum to Dayton, KY, could also greatly help solve access and congestion issues on the east side of the region.
ODOT officials say that the online survey will remain open until Wednesday, June 15. After this evening’s open house in Mt. Lookout, the next meetings to take place in Fairfax and Mt. Washington will occur on May 4 and May 5, respectively.