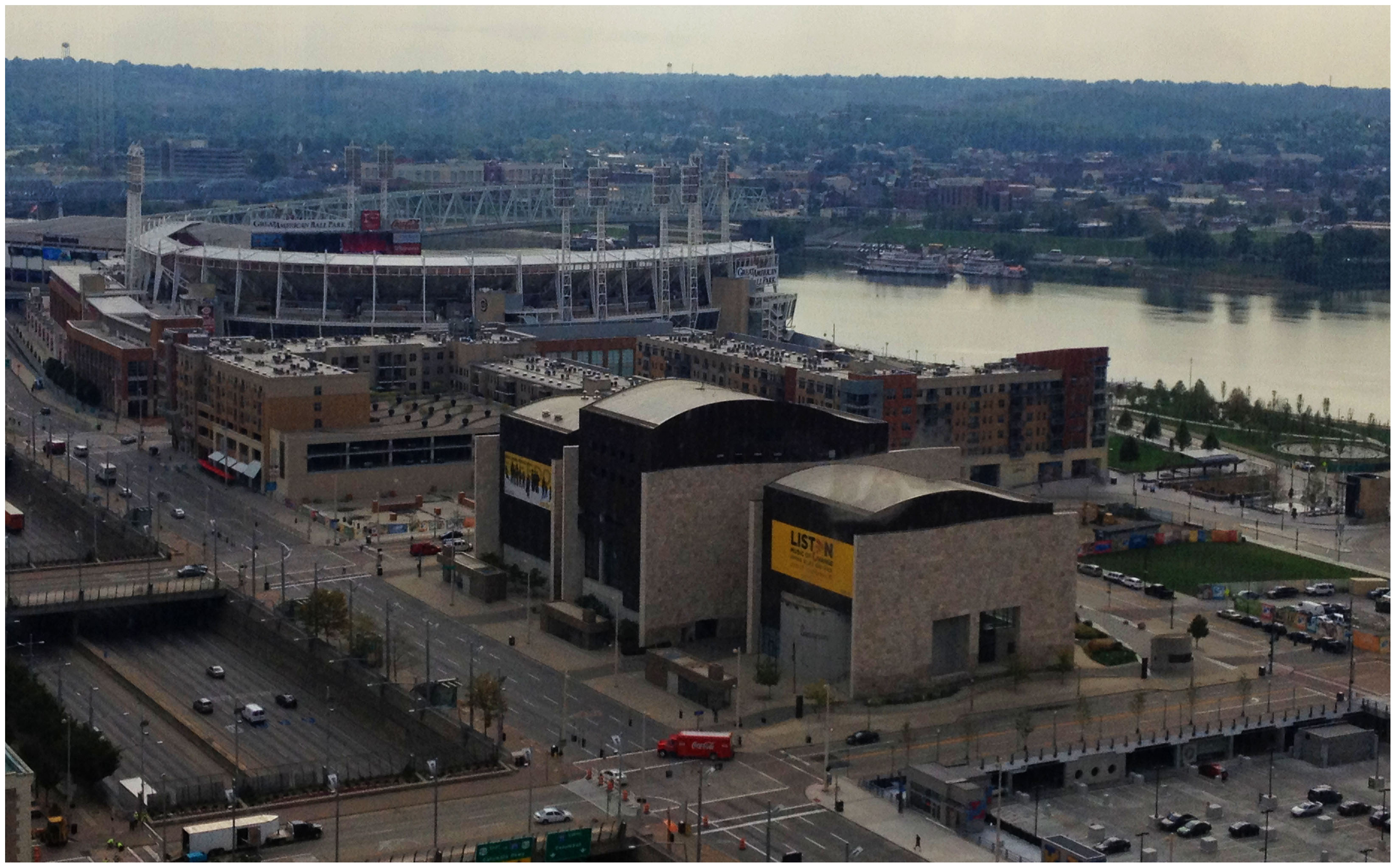
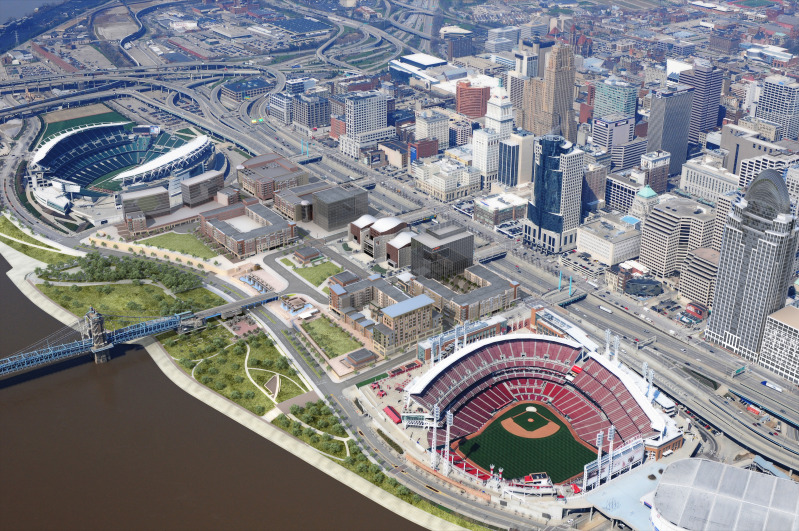
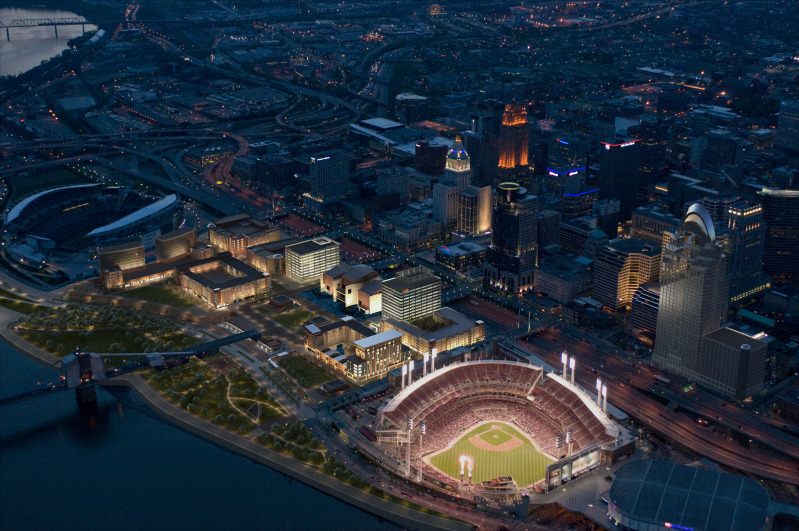
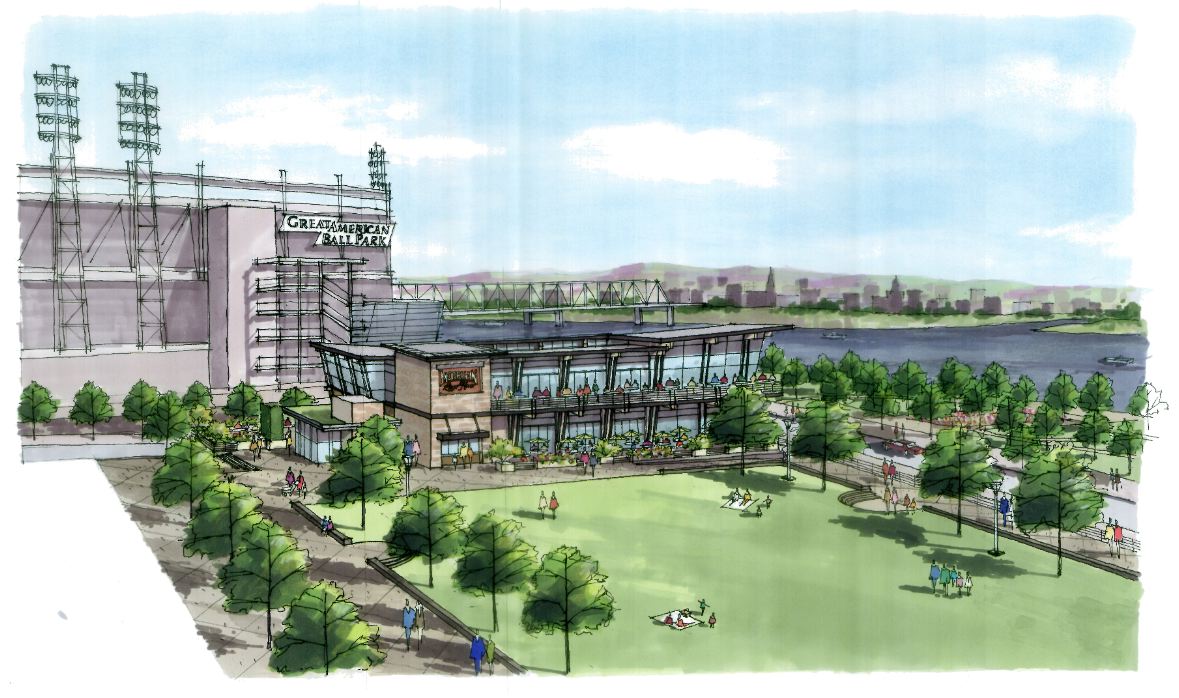
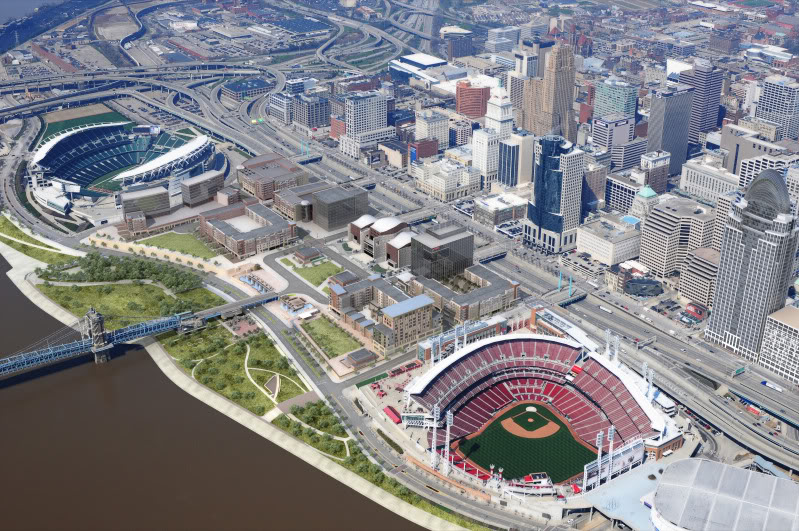
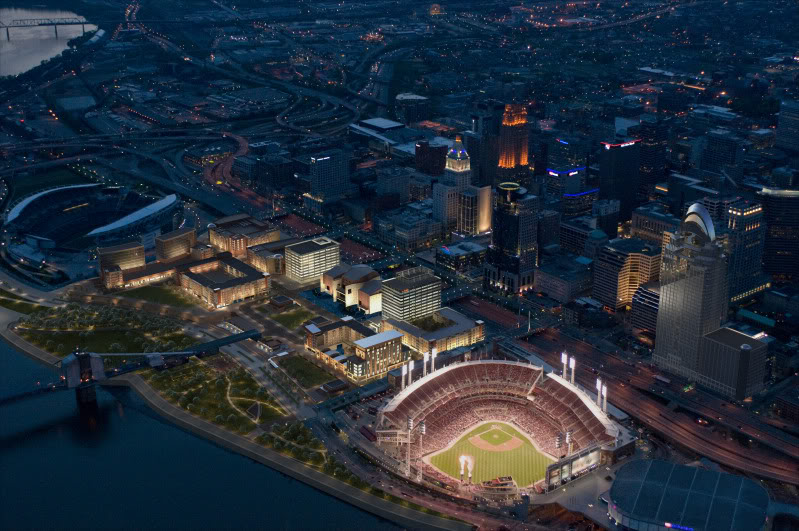
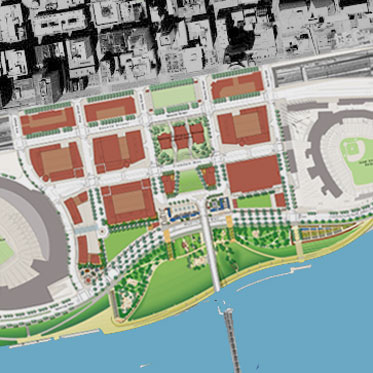
Billions of dollars of public and private investment has transformed Cincinnati’s central riverfront over the past decade. What was once a flood-prone industrial center turned unusable waterfront property, is now home to a new park, neighborhood, museums, and professional sports venues.
The investments made to date have been so successful, in fact, that they are creating spinoff investment in the Central Business District. A remaining hurdle, however, is the crossing of Third Street, Fort Washington Way (FWW), and Second Street.
The nearly 300-foot span of roadways was significantly reduced in width when Fort Washington Way was reconstructed in 2001, but the span remains a visual barrier for many of those in the Central Business District or at The Banks.
 Cincinnati officials are looking to build off of recent success by capping Fort Washington Way. Photograph by Randy A. Simes for UrbanCincy.
Cincinnati officials are looking to build off of recent success by capping Fort Washington Way. Photograph by Randy A. Simes for UrbanCincy.
The problem was expected by city officials, in the 1990s, during original planning efforts for the central riverfront’s transformation. As a result, city leaders worked to raise $10 million to construct pile foundations that could one day support a cap over the interstate highway running beneath street level on FWW.
The pile foundations are capable of extending 600 feet over the highway roughly between Elm Street and Main Street. According to engineers who worked on FWW’s reconstruction, the caps could support the weight required for a park, or built structures depending on height and building materials.
No specific development plan for the caps has been developed however, and now the city is launching a design competition called Connect the Blocks to establish a vision for space.
“The Banks is well underway, downtown is growing, and now we must begin thinking about what we as a community want to see over Fort Washington Way to connect downtown and the riverfront,” City Manager Milton Dohoney stated in a prepared release. “We must first have a common vision of what we want, then we can establish the roadmap to get there.”
The national competition is calling on architectural, engineering and design professionals to create and submit concepts and cost estimates for the caps that are to be built over FWW. According to city officials, three to five finalists will be selected and awarded stipends to further refine their designs.
St. Louis has dealt with similar issues as it has tried to bridge the divide created by I-70 between downtown and the Gateway Arch grounds. While I-70 will not be capped entirely, a one block portion is envisioned to connect Jefferson National Expansion Memorial with Kiener Plaza in the CityArchRiver 2015 plan.
In Ohio, the only similar example of such a project exists in Columbus where a $7.8 million cap was constructed over I-670 along N. High Street. It includes approximately 25,000 square feet of street-level retail and connects Columbus’ downtown with its Short North district.
The City of Cincinnati held the first of two public meetings, on the design competition, last Wednesday in Madisonville. The second meeting is scheduled to take place on Tuesday, October 9 at 6pm at the Main Public Library (map). The public is also invited to weigh in on the process by participating in an online survey going on now, and officials also say that the public will be invited back to view the finalists’ designs once they are selected.
Full details about how to participate in the eight-month design competition can be found on the project’s website. The implementation of any winning design, officials say, will be dependent upon the availability of funding.