While two of the more lengthy discussion items were controversial planned commercial developments in Hyde Park and Roselawn, Cincinnati Planning Commission had a slew of other items on their Friday afternoon agenda.
In three related moves, the City Planning Commission recommended using Interim Development Control Overlay Districts. Two were extensions of existing IDCs, but one was newly recommended. Traditionally the City uses IDCs to put a temporary control on development while planning or feasibility studies are conducted. During such time, the establishment of uses, construction of new buildings, and the demolition or alteration of existing structures are all subject to review by the City Planning Commission.
The two recommended for extension include IDC Districts 73 and 74, Wasson Line District and Pleasant Ridge NBD, for an additional six months to allow for the completion of land use and zoning studies.
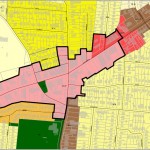
The newly recommended IDC is for the hot real estate market surrounding the University of Cincinnati. In particular, the neighborhoods to the south and southwest of the university where midrise developments continue to be proposed and built, much to the dismay of many long-time residents.
IDC District 77 was recommended to be put in place for a period of three months while a University Impact Area Study will look at growth and housing conditions, parking and traffic, quality of life concerns, and new development vs. existing character in the areas within a quarter-mile walk from the university’s main campus and the Clifton Heights business district.
Here is a quick rundown of the rest of the cases and the recommendations made by the seven-member board:
- Approved the sale of 1623 Pleasant Street in Over-the-Rhine to Avila Magna Group, LLC for $20,000. The developer plans to renovate the 3,296-square-foot building into three one-bedroom for-sale units and one two-bedroom for-sale unit.
- Approved the sale of approximately three acres of land left over from the Kennedy Connector road project to Vandercar Holdings and Al Neyer Inc. for $530,000. The developers plan to consolidate the land with adjacent parcels to construct two office buildings of up to 45,000 total square feet.
- Approved a dedication plat of 3.48 acres along the south side of River Road in Sedamsville to allow for a western extension of the Ohio River Trail.
- Approved a final development plan for Phase 1G of Oakley Station, which will consist of a 12,000-square-foot multi-tenant retail building at the northwest corner of Vandercar Way and Oakley Mill Lane.
The commission also approved the sale of a one-acre parcel at Eighth and Sycamore streets to the Cincinnati Center City Development Corporation for $1. This move will ultimately pave the way for a new $45 million development that will continue the transformation of the northeast quadrant of the central business district where numerous other midrises are advancing.
Through the agreement, the non-profit development corporation will create a garage air lot, a commercial air lot, and an apartment air lot. Once construction is imminent, 3CDC will sell the garage air lot to the City for $1 to allow for a 500-space parking garage to be built. They will then sell the apartment air lot to North American Properties for $1 for the construction of a 130-unit tower, and will retain ownership of the commercial air lot for the construction of 10,000 square feet of commercial space.