With National Bike Month coming to a close, the rhetoric surrounding the fate of the city’s lone protected bike lane continues. Following weeks of discussion and political wrangling, the city’s latest politicized transportation project will be studied again after two initial reports were found to be inconclusive by some leaders at City Hall.
The debate is, perhaps not coincidentally, taking place while the city’s bike community is becoming more active in terms of numbers of riders, group rides and political activism.
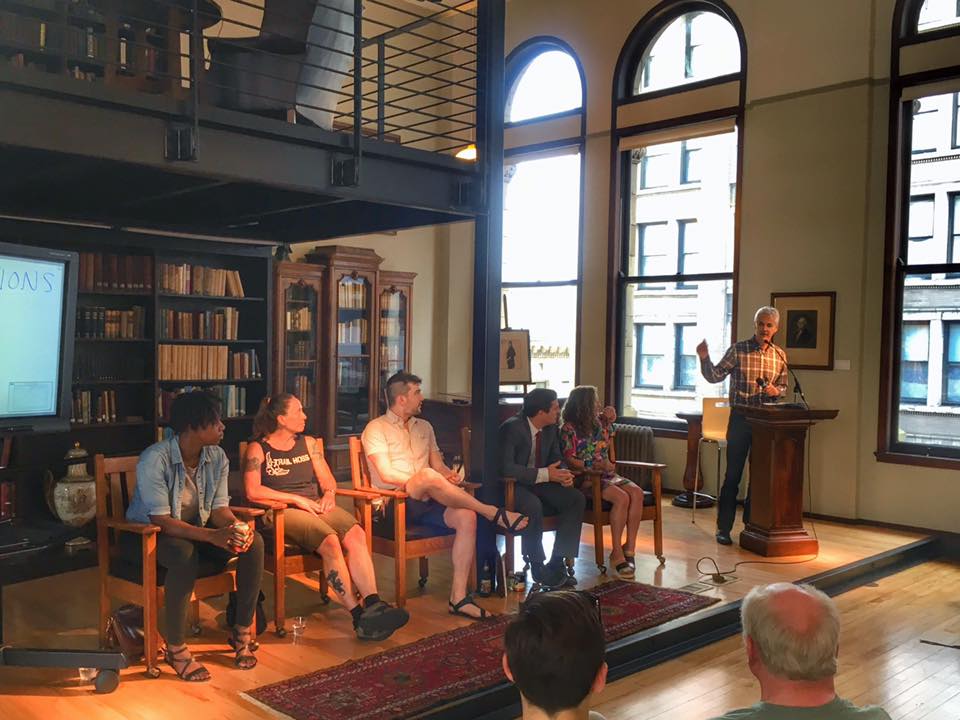
Last night at the Mercantile Library dozens crowded the venue to hear a panel discussion and engage in discussion about the current and future state of Cincinnati’s bike network. Organized by Queen City Bike and other area advocacy groups, the event served as an opportunity for people to constructively discuss the good and bad about the city’s bike infrastructure.
First adopted in June 2010, Cincinnati’s Bicycle Transportation Plan has served as the official document meant to guide policy decisions at City Hall. Since its adoption, however, the planning document has largely sat on the shelf, with targets for the development of bike lanes and other infrastructure falling behind schedule.
Mayor John Cranley’s administration has made it very clear that they are not interested in the development of on-street bike lanes, particularly those that are physically protected from automobile traffic. In lieu of pursuing those targets, the Cranley administration has instead focused on off-street bike trails; while also providing the critical upfront investment to launch Red Bike.
“Under our public-private relationships and support of council and a very vibrant cyclist community, in my opinion, we’re going to be the most bike-friendly city in America in four years,” Mayor Cranley told Aaron Renn in 2014. “We have three major bike trails that can be connected on abandoned train tracks into downtown; and, candidly, we intend to get all three of them build in the next four years. There’s just nothing like it in any city.”
National studies have found that protected on-street bike lanes not only provide the greatest level of safety for both bicyclists and motorists, but also encourage a greater range of demographics to bike. According to the American Journal of Public Health, this is largely attributable to the fact that streets with protected bike lanes saw 90% fewer cyclist injuries per mile than those without.
When it opened in July 2014, the Central Parkway protected bike lane was the first of its kind in Ohio. Since then other cities around the state have developed their own protected bike lanes, but Cincinnati has gone back to discussing the merits of the project after a handful of motorists complained that it made the roadway more dangerous and confusing to navigate.
Those suggestions were refuted in a report issued earlier this month that found conflicts along the 2.2-mile stretch of Central Parkway with the protected bike lane are no different, or even safer, than on other comparable streets around the city; but that further experience and education is needed for motorists.
“The Cincinnati Police Department and DOTE both believe that as drivers, cyclists, and pedestrians become more familiar with the area and with the rules for the bike lane operations, there should be fewer conflicts,” the report concluded. “DOTE will continue to monitor conditions, and improvements may be made in the future as best practices evolve.”
Whether the future of Cincinnati’s bike infrastructure continues to focus on off-street bike trails, or shifts to a more balanced approach is yet to be seen. Queen City Bike is hoping last night’s event, and others to come in the future, will help grow the number of people advocating for a more robust bike network, but also refine the vision based around what it is the community wants to see pursued.
The Cranley administration has put forth a proposed budget that increases spending on bicycle infrastructure, but the overwhelming majority of that money has been tagged for off-street trails, not protected bike lanes or other sorts of infrastructure improvements.
City Council has until the end of June to review, make proposed changes and approve next year’s budget. This will give the growing bike advocacy community a strong opportunity to make their voices heard.