As Cincinnati moves forward with the development of the Midwest’s first modern streetcar system, a political leader is pushing for even greater transit improvements that would compliment an increasingly diverse collection of alternative forms of transport.
Cincinnati Vice Mayor Roxanne Qualls is proposing a robust network of bus rapid transit (BRT) that would connect the region’s commuters with major employment centers like Uptown and Downtown. Qualls believes BRT is a cost-effective and innovative transit strategy.
“Bus rapid transit incorporates many of the advantages of light rail, but is cheaper and can be implemented quickly,” Qualls said in a prepared statement. “Cities around the world and the country are giving commuters a great transit option now with rapid transit.”
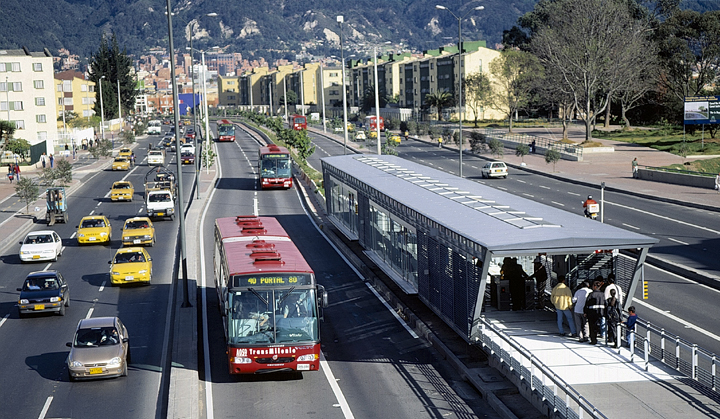
Many cities around the United States and internationally are beginning to look at BRT more closely as a cheaper alternative to building dedicated rail transit systems. After first being popularized in Bogotá, Columbia, bus rapid transit now exists in 33 cities throughout the world with an additional 22 systems planned.
What differentiates BRT routes from other bus routes is the dedicated lanes they use. These dedicated corridors are often complimented by signal prioritization and timing that allows for faster travel times over long distances.
“Cities are looking to rapid transit to meet increased commuter demand and to spur development,” Qualls stated. “Because the conversion to rapid transit is faster and cheaper than developing light rail, it is an important interim step that helps build transit ridership and provides a great service in the near term.”
While some transit experts agree that BRT can serve as an integral part of an overall transit system, others believe that BRT can be compromised when pitched as an inexpensive alternative to light rail.
“If you look at Oakland, who was studying BRT, they’ve been working on the project for a long time and recently had the City of Berkeley decline to even study dedicated lanes even though that was the plan all along,” explained Jeff Wood, Chief Cartographer, Reconnecting America. “They felt like they could do it cheaper than light rail, but now they aren’t even going to get any of the benefits of bus rapid transit.”
As part of Vice Mayor Qualls’ motion, BRT would be a portion of a larger multi-modal transit plan that would include the streetcar and light rail according to Cincinnati’s existing rail plan. Major corridors would include I-75, I-71, Queen City Avenue, Harrison Avenue, Vine Street, Reading Road, Madison Road, and Martin Luther King Drive. Qualls suggested the city aggressively pursue state and federal funds to pay for the development of bus rapid transit.
Those interested in learning more about bus rapid transit have the opportunity to meet with BRT expert Jack Gonsalves at the OKI Regional Council of Governments Board Room (map) on Monday, December 6 at 1pm. Gonsalves will be joined by a variety of local leaders to discuss BRT and how it might be developed in Cincinnati.