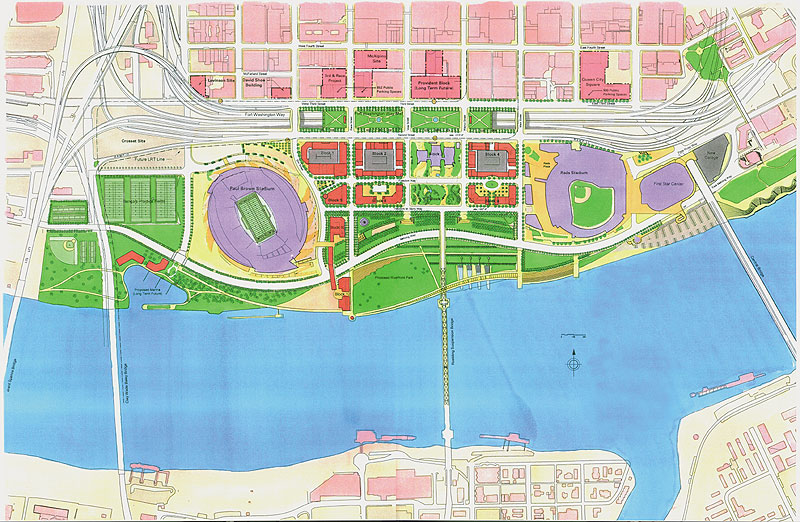
Fort Washington Way might be better known to some Cincinnatians as the I-71/US-50 trench through downtown Cincinnati, but few might know the full story behind how the current area came to be what it is today. Every Wednesday this July, UrbanCincy will cover a part of the history of Fort Washington Way, its construction, the political fights that came with it, and the potential future for the area. Furthermore, the unprecedented foresight that the engineers, politicians, and public alike demonstrated through the construction will be highlighted.
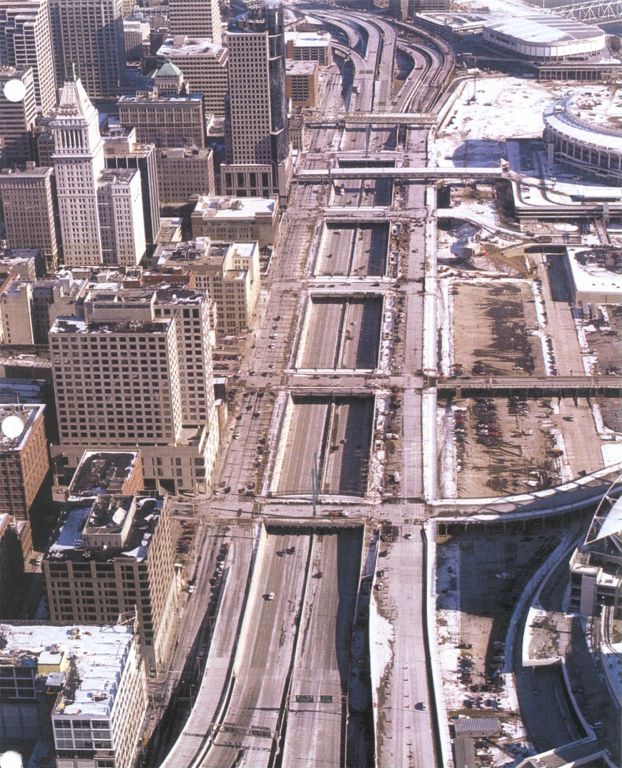
The City of Cincinnati developed where it is today because of its location on the Ohio River. The river served as the primary economic engine for the city and therefore the larger region. As such, the fact that Fort Washington Way bisects the urban core from the riverfront troubles individuals who wish to see the city become whole once again. However, it is important to remember what the stretch of land looked like prior to major renovations a decade ago.
In 1998, construction began on the approximately 1.25-mile stretch of highway. Originally, the plan included burying the stretch of highway completely in order to hide the highway eyesore from the remainder of downtown. However, that idea was overturned in 1996 because many people wanted to ensure that visitors to the city would be able to see it as they traveled through. New plans were completed and construction began.
In 1999, after more than two-thirds of the renovations were complete, there was renewed interest in burying the highway. Proponents claimed that a buried highway would ensure an uninterrupted transition from downtown to the riverfront. The engineers knew that they wouldn’t be able to finish the project on time and on budget if they changed the project so late, so they compromised by sinking the roadway below the level of the rest of downtown’s street grid. Part of this compromise included driving extraordinarily strong support piles into the ground that were engineered to hold caps that could eventually cover the highway if the decision was made to do so at a later date.
The current gaps between segments of the street spanning over Fort Washington Way are spaced such that caps 600 feet wide could be installed with relative ease and with a gap between segments. Gaps ensure that the area is not officially a tunnel, and as a result, the dangers and costs associated with the fire safety precautions of a tunnel are avoided. Engineers state that the pilings supporting the caps could withstand the weight of several feet of dirt, making an unique and exciting urban park possible. Furthermore, the caps could support the weight of buildings approximately four stories high. The latter options would provide the opportunity to link The Banks development with the rest of downtown abutting the current trench.
The major change in the 1998 redesign came by untangling and streamlining the mess of highway on- and off-ramps. Doing so allowed the roadway to carry a greater capacity, increase safety, and dramatically decrease the total width of Fort Washington Way. Once construction was completed, about 40% of the original width was gone as a result of the better design. The space that was saved freed up room for the Great American Ball Park, National Underground Railroad Freedom Center, Paul Brown Stadium and much of The Banks development.
In the next three weeks, UrbanCincy will highlight how this transformation took place. In the process, we will show how the city demonstrated an unprecedented level of foresight, saving current and future taxpayers untold sums of money. The inter-jurisdictional cooperation that this project achieved set the stage for the redesigned area to win more than a dozen national and international awards.
As one engineer told me: “We weren’t highway building. We were city building.” Check back each Wednesday in July to learn more about how Fort Washington Way project impacted current and future development.