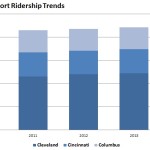
While transit ridership nationwide inched upward and reached its highest level in more than a half century, it remained flat in Ohio’s two largest metropolitan regions.
According to new data released by the American Public Transportation Association (APTA), transit ridership in both Cincinnati and Cleveland remained essentially unchanged from 2013 to 2014. With a 3% ridership gain over the previous year, Columbus bucked the trend and posted the fifth highest bus ridership gain nationally.
“In 2014, people took a record 10.8 billion trips on public transportation — the highest annual ridership number in 58 years,” said Phillip Washington, APTA Chair and CEO & General Manager of the Regional Transportation District in Denver. “Some public transit systems experienced all-time record high ridership last year.”
In a nod to Columbus, Washington said that the increases were not just relegated to large cites, but were found in smaller and medium size communities as well. But according to Streetsblog USA, an UrbanCincy content partner, the national increases can be largely attributed to the large gains in New York City, which accounts for roughly 25% of American transit ridership.
Growth in transit ridership is expected to continue in the years ahead as dozens of cities throughout the United States build out regional rail networks and implement new bus services. In Cincinnati, that includes new services operating out of the recently opened Uptown Transit District and the forthcoming Northside Transit Center and Walnut Hills Transit District.
The opening of the first leg of the Cincinnati Streetcar is also expected to boost ridership in 2016. Until then, Cleveland will remain as the only city in Ohio to have both bus and rail offerings. Not surprisingly, Cleveland’s transit usage dwarfs that of both Cincinnati and Columbus.
While year-over-year ridership only increased nationally by 1%, that gain is seen as encouraging since it occurred at the same time as prices for gasoline plummeted. Transportation officials see continued transit ridership growth, in addition to VMT growth for the first time in nearly a decade, as a clear indication of a much stronger economy where more people are employed.
“Since nearly 60 % of the trips taken on public transportation are for work commutes, public transportation ridership increases are seen in areas where the local economy is growing,” said APTA President and CEO Michael Melaniphy.
In spite of Cincinnati’s growing economy, transit ridership actually posted a slight loss. That loss, however, is in line with national bus ridership trends. While Cincinnati saw an annual decrease of 1.8%, bus ridership across the country also experienced a 1.1% decline. All modes of rail transit, meanwhile, posted gains, which now accounts for 46% of all trips made by transit.
Light rail systems posted the biggest annual gain of 3.6%, while heavy rail and commuter rail added riders by 3.3% and 2.9%, respectively.
“People are changing their travel behavior and want more travel options,” Melaniphy concluded. “In the past people had a binary choice. You either took public transit, most likely a bus, or you drove a car. Now there are multiple options with subways, light rail, streetcars, commuter trains, buses, ferries, cars and shared use vehicles.”
EDITORIAL NOTE: APTA’s annual report does not include ridership data for the Transit Authority of Northern Kentucky (TANK), which provides approximately 3.8 million trips annually. For the purposes of this analysis, UrbanCincy has used a constant 3.8 million annual trips from TANK in the Cincinnati totals presented in the above chart.