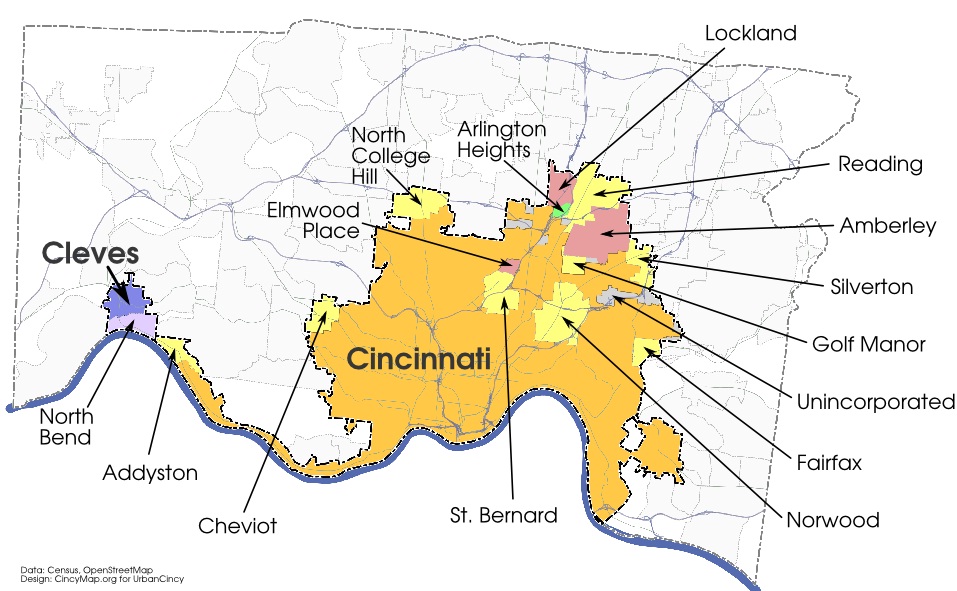
For years local officials and civic boosters have been calling for the merging of local government operations. A core issue that has not been discussed, however, is that of merging local municipalities entirely.
In Hamilton County there are 49 different political jurisdictions ranging from a few hundred people to approximately 300,000 in the City of Cincinnati. That is approximately 16,334 people per political jurisdiction. Certainly we are not serving our residents in the most effective and prudent way when there is so much fragmentation.
Many of the smaller communities, with just a few hundred a couple thousand people, have recently fallen on more difficult financial times. Both Arlington Heights (population 745) and Elmwood Place (population 2,188) have been embroiled in scandals revolving around their use of speed traps and cameras to generate revenue.

Smaller jurisdictions throughout Hamilton County should be merged with larger ones like Cincinnati and Cleves. Map by Nate Wessel for UrbanCincy.
In Arlington Heights the scandal revolved around the stealing of $260,000 of public money, and in Elmwood Place it involved an abusive use of traffic cameras to issue tickets.
“The Village Council needs to seriously consider dissolving the Village of Arlington Heights,” Hamilton County Prosecutor Joe Deters proclaimed after the two theft indictments. “The Village seems to be nothing more than a speed trap with no checks and balances…Consolidating with another political subdivision is long overdue.”
In other cases, like Silverton (population 4,788), the jurisdictions have become so small that they can no longer be considered a city.
There are certainly some efficiencies to be gained by merging local police and fire departments in smaller communities throughout our region, but merging entire municipalities will reap much bigger savings.
In Hamilton County, some 15 communities could be easily folded into the City of Cincinnati. Many of these municipalities already are served by Cincinnati Public Schools and are either adjacent to, or completely surrounded by, Cincinnati’s city limits.
Most of these 15 municipalities have less than 5,000 people, and would surely benefit from the much broader public services offered by the City of Cincinnati. Larger cities like Norwood (population 19,207), Reading (population 10,385), and Cheviot (population 8,375) would also see improved public services and improved financial stability.
Furthermore, it would put an end to the many economic development incentive battles that are waged across these arbitrary political boundaries.
Each of the 15 communities could continue to maintain its identity by becoming a new official neighborhood within the City of Cincinnati, which would see its population grow by more than 77,000 people as a result, as they essentially function now in the region’s urban fabric. This would allow these places to stay true to their roots while also gaining more political clout, improved financial stability and public services, and expanded opportunities within a much larger political jurisdiction.
State budget cuts are continuing to cut into the core of local public operations, and at some point each of these communities will reach a point where “belt-tightening” will no longer achieve the savings needed to remain financially productive.
Plus, if you community’s sole purpose for maintaining its separate political jurisdiction is to maintain those positions, then it might be time to rethink your reason for being.