Unsurprisingly, Ohio Secretary of State Jon Husted (R) has sided with his fellow Republicans in Hamilton County and cleared the way for Hamilton County’s Board of Election offices to move from Downtown to Mt. Airy. The ruling came as a result of the Hamilton County BOE’s deadlocked vote on the matter, which went along party lines.
Such a move will not happen for several years, but when it does it will make Hamilton County the only urban county in Ohio without its election offices located in its downtown.
Democrats seem to fear that the move will make early voting more difficult for the tens of thousands of residents who do not own a car. Republicans, on the other hand, seem giddy with the prospect of the new site being surrounded by an abundance of “free” surface parking options.
So what would the move mean for those living without a car in Hamilton County? In short, it would make voting a lot more difficult – especially for those in the eastern part of the county. It would also mean that the elections office and lone early voting location for Hamilton County would be moving further away from the population center and where most people work.
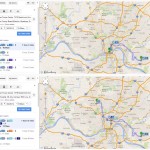
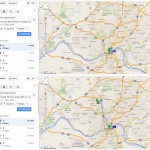
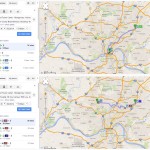
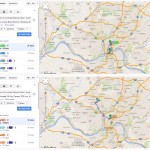
Those coming from the transit center at Anderson Towne Centre would see a four-hour round-trip, if they made all of their transfers seamlessly and nothing ran behind schedule. Those in the center city, the most densely populated area in the county, would need to block out several hours to account for the two-hour round-trip journey from Government Square.
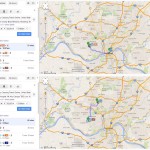
If you are trying to get to the new Mt. Airy location from the Glenway Crossing Transit Center, Uptown Transit District or Kenwood Towne Center, your travel time would largely remain unchanged. That is if those people lived within a close walk to those transit centers like those near Government Square. The reality is that each of those three areas are much less walkable and would take considerable time accessing on their own right, thus adding significantly more time to the journey.
Should Greg Hartmann (R), Chris Monzel (R) and Alex Triantafilou (R) move forward with this it will in fact make the elections office and lone early voting location more accessible for those with cars in the western and northern parts of Hamilton County. It would also, however, make it less accessible for those with cars in the central and eastern parts of the county, and also worse for those without a car at all.
What is troublesome is that those with a car have access to the existing site. Yes, they may have to pay to park, but that is a minor inconvenience that absolutely must be weighed against creating hours-long journeys for those without a car.
The burden would be shifted to those who already have the least in our community. We hope Hartmann, Monzel and Triantafilou realize this would be morally wrong and decide to keep non-back office and early voting operations of the Hamilton County Board of Elections downtown.