According to the Federal Reserve Bank of Cleveland’s annual survey of its district, jobs and the economy overall continue to remain the top concern for local leaders.
Each year, seeking to gauge ground-level concerns and needs, the Federal Reserve Bank of Cleveland – which includes all of Ohio, Eastern Kentucky, Western Pennsylvania, and the West Virginia Panhandle – conducts a survey of community leaders to assess local challenges around the Fourth District.
In their 2015 survey, jobs remained the number one concern and priority for local leaders throughout region. Skyrocketing to the second place position was a preoccupation with access to quality and affordable housing; while vacant and abandoned properties were third.
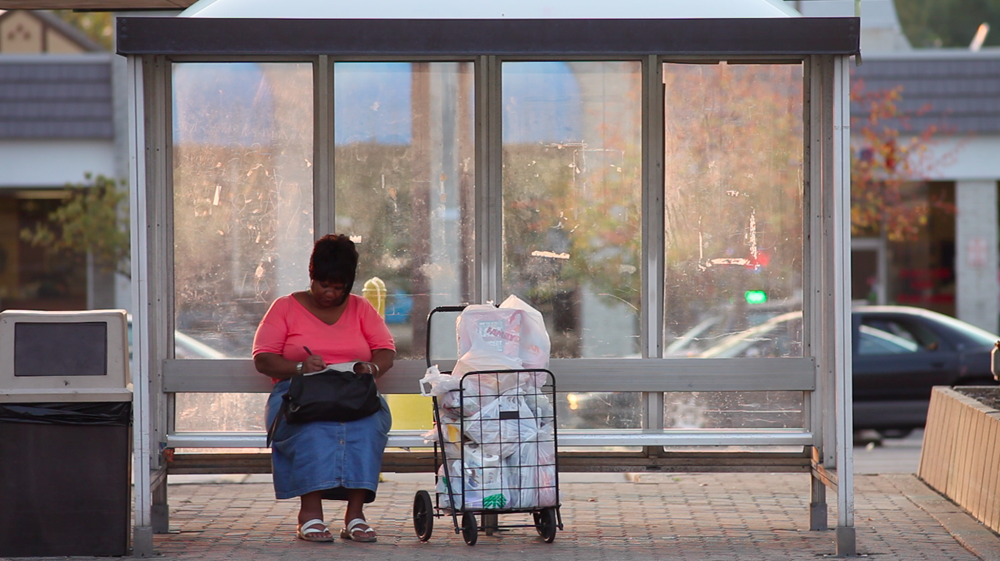
While public officials acknowledge that jobs are indeed being created, the concern is about the type of job creation that is occurring in their communities. Part-time jobs, low wages, lack of benefits, and high turnover mean that being able to support a family is out of reach for many of those working in these newly created positions.
There is also growing concern about continued vacancy in high-wage, high-skilled positions where a skills gap is keeping many of those looking for work from filling these positions.
New in this report is the growing concern over affordable housing. While low-wage and part-time jobs continues to grow, new housing options are limited and those that are being developed are often either at the high or low end of the market. Economists at the Federal Reserve Bank of Cleveland say this is the first time the issue has registered as a top concern.
Continued in-migration to central cities, like what is being experienced in Cincinnati, is exasperating this problem throughout the Fourth District. Of course, this in-migration is seen by many as a net positive, even though the housing market has yet to catch up.
“The remarkable resurgence happening in core neighborhoods will have a very positive effect on those neighborhoods, and on the City of Cincinnati overall,” explained a professor at the University of Cincinnati in response to this survey.
A social services organization CEO in Pittsburgh also sees increasing migration to urban centers positively, but worries about the possibility of rising property driving historic residents from their neighborhoods. The concern over affordable housing is, as the Cleveland Fed puts it, “respondents grappling with the good and bad elements of revitalization occurring in their urban centers.”
While less relevant in the Cincinnati region, the Fourth District’s shale gas boom has also caused affordable housing problems in parts of West Virginia and Western Pennsylvania, as oil workers move in and are able to pay more in rent than other, longer-term residents.
Although the economic recovery is in full swing and most cities are seeing migration to their urban centers, many neighborhoods are still suffering from blight and disinvestment. According to the survey, abandoned properties were the third most-cited concern among respondents. Many cities in the region, particularly those in northern Ohio, are still saddled with significant amounts of abandoned and vacant properties, many of which left over from the housing crisis.
These properties not only require tax revenue to maintain and produce no tax revenues in return, but they are also most typically found in low-income, minority neighborhoods, exasperating already-difficult economic conditions for many of these communities.
At the end of the survey, the Cleveland Fed attempted to gauge emerging issues, both positive and negative. The biggest negative issue cited by almost all respondents was how to deal with an aging infrastructure that needs to be replaced. Budget cuts at all levels of government have lead to increased deferral of basic maintenance and improvements, especially in older municipalities that dominate the Fourth District.
While on the positive side, most respondents cited the continued migration of residents to the inner-city as having the most potential to positively impact economic recovery throughout the region.
Respondents also specifically mentioned the activation of the National Housing Trust Fund, which will provide federal support to help areas construct, preserve, and rehabilitate buildings for affordable housing. The National Low Income Housing Coalition predicts that Ohio and Pennsylvania will be some of the largest recipients of these funds, and thus have the most to gain or lose by its status.