Amidst further positive national news for upgraded Midwestern rail service, All Aboard Ohio met in Cleveland for their summer meet-up. At the weekend-long gathering, the group toured the Greater Cleveland Regional Transit Authority’s numerous heavy rail, light rail, and bus rapid transit lines.
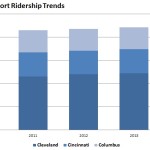
Often unknown to outsiders, the Cleveland area boasts some 39 miles of rail transit, with daily ridership of over 53,000. As a result, Cleveland’s transit ridership dwarfs that of both Cincinnati and Columbus. Even though Cleveland is approximately the same size as Cincinnati and Columbus, its transit ridership is bigger than both of them combined.
In addition, All Aboard Ohio executive director Ken Prendergast led the tour and showcased the substantial amount of transit-oriented development that is taking place throughout Cleveland.
With the opening of Cincinnati’s first few miles of rail transit just over a year away, it made the tour particularly relevant. As a result, I was joined by a small Cincinnati contingent including City Councilman Chris Seelbach (D), SW Ohio Director of All Aboard Ohio Derek Bauman, and Price Hill community leader Pete Witte.
The group’s tour began at Terminal City Tower in downtown Cleveland, where inter-city trains once stopped and all rapid transit lines currently meet. From there we took the Green Line to the lakefront, passing large-scale transit-oriented development along the Cuyahoga River, the Port of Cleveland, Cleveland Brown Stadium, Rock & Roll Hall of Fame, and the city’s Amtrak station.
Negotiations are currently underway for the construction of a large intermodal hub where Amtrak is currently located, combining Amtrak, Greyhound, Megabus, and many local buses from Akron and other cities into one complex.
The Green Line’s E. 55th Street Station was showcased after having been rehabbed in 2011. It is part of GCRTA’s program to rebuild every station in its system. Nearby this still young station, an old hospital is undergoing a $75 million redevelopment that will refit it with apartments.
Changing to the Blue Line, the train ran through semi-suburban areas that reminded the Cincinnati contingent of the Wasson Corridor. Among these areas is the Van Aken District at the Warrensville Station at the end of the line. There, Joyce Braverman, the planning director for Shaker Heights, gave us a walking tour of the area and detailed the numerous transit-oriented developments currently under construction, including a $91 million residential development and a rebuild of a pedestrian-unfriendly intersection.
A newly renovated station – just four days old – greeted us at Little Italy along with the Feast of the Assumption Festival. In addition to the throngs of neighborhood residents filing in and out of the trains, redevelopment can be found nearby in University Circle. During an opportunity to speak with the president of University Circle Inc., he boasted about the area’s transformation from a run-down district with multiple surface parking lots into one of the city’s most desirable neighborhoods.
The numbers back up the claims. In just a decade, more than $6 billion in private investment has flowed to the neighborhood, generating some 10,000 new jobs and 11,000 new residents.
While serviced by RTA’s Red Line, this particular area is also anchored by Cleveland’s now famous Health Line BRT, which runs along Euclid Avenue to the center city and is the highest-rated BRT line in North America.
Through this station rebuilding program, Cleveland has used it as an opportunity to leverage an impressive amount of private investment in the surrounding areas. While success of downtown Cleveland has been well-publicized amidst the continued struggles elsewhere in the region, there are bright spots popping up along the city’s transit corridors. With more than 100 rail and BRT stations in the region, many more opportunities seem to be on the horizon.